Build > Reference > app_settings.json > .sms
SMS Settings: Instructions and schema for defining SMS settings
Integration for sending and receiving messages
As of v3.11.0, messages can be sent and received using RapidPro as a messaging gateway.
Generate a long unique key to use as the cht_api_key.
Log in to your RapidPro dashboard, go to the globals page (/global/) and create two globals with the following data:
cht url, value: https://<your-cht-instance-host>/api/v2/sms/rapidpro/incoming-messages. For security the instance host must not include basic authentication. (NB: This endpoint was added in CHT 4.1.0. If integrating with an earlier version you will need to use the earlier version with a typo in the URL: https://<your-cht-instance-host>/api/v1/sms/radpidpro/incoming-messages)cht api key, value: <cht_api_key>Note
Please note that only letters, numbers, and hyphens are accepted when naming a global variable in RapidPro. However, any space(s) in the name will be replaced with underscore(s) when saved.
For example, cht url will be saved as cht_url.
The names of these two global variables are arbitrary, but in this document we will keep referring to the names defined above.
Now visit the RapidPro workspace settings page (/org/home/) and check your RapidPro API token (we’ll refer to this as the rapidpro_api_key). We will use it later.
In your RapidPro dashboard, visit the flows page (/flow/) and create a new flow. It only needs to contain a webhook, to relay the message to your CHT Core instance and handle possible errors.
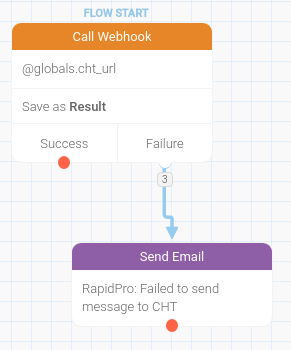
flow_overview
Configure the new webhook:
POST to the cht_url you configured earlier: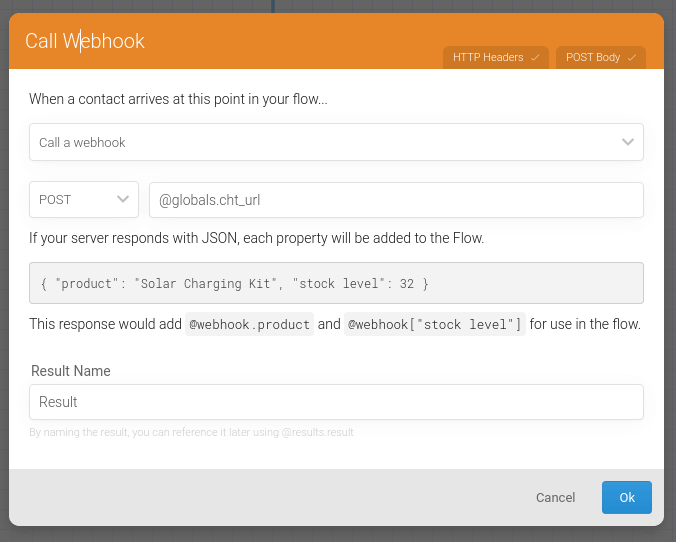
flow_webhook_host
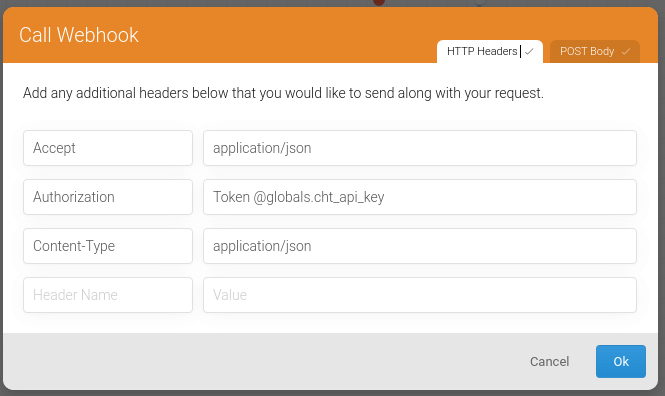
flow_webhook_headers
@(json(object(
"id", run.uuid,
"from", replace(urns.tel,"tel:+", "+"),
"content", input.text
)))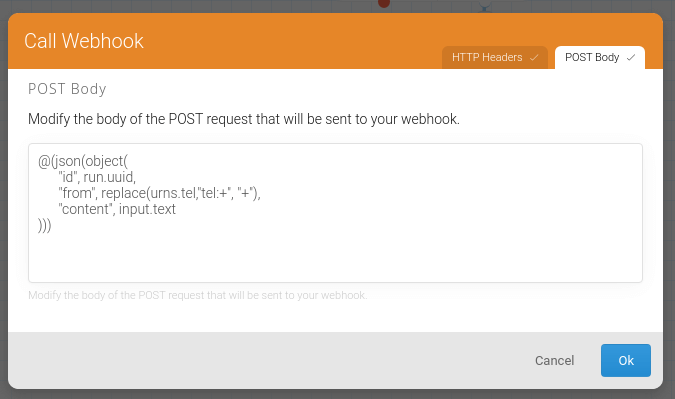
flow_webhook_body
Create a trigger (/trigger/) to start the new flow when a message is not handled elsewhere.
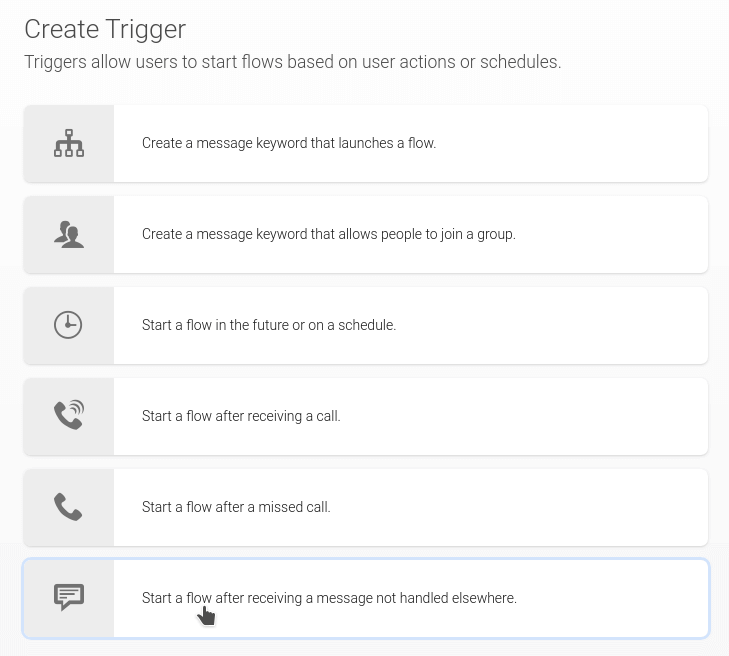
trigger_select
For more details about RapidPro configuration, consult the RapidPro integration documentation.
The RapidPro integration uses the CHT Credentials service to retrieve the API keys using the IDs rapidpro:incoming and rapidpro:outgoing. Use the CHT credentials API to securely store the credentials.rapidpro:incoming should contain the value of the long unique key generated earlier <cht_api_key> to verify incoming requests from RapidPro.rapidpro:outgoing should contain your RapidPro API token <rapidpro_api_key> to authenticate requests made against RapidPro’s API.
Update your app settings as follows.
{
"sms": {
"outgoing_service": "rapidpro",
"rapidpro": {
"url": "<RapidPro instance url>"
}
}
}Important
The RapidPro API endpoints are rate-limited, meaning that requests to send or check the status of messages beyond a certain number per hour will be blocked. The limit is currently 2500 actions per hour, and may change without notice. Check out the RapidPro API reference for more details. If sending a message or retrieving a status update fails, it will be retried automatically again later.
When the outgoing message service is set to RapidPro or the host/account are changed, CHT Core will request state updates for all messages that aren’t in one of the final states: delivered, failed, denied, or cleared. Each of these request counts towards your quota. Since the messages are unlikely to exist on the new RapidPro service, these requests will fail on every retry and consume your request quota. It is therefore important that all outgoing messages have a final state before switching RapidPro accounts or hosts. The status can be set to failed for messages that should not be resent without user intervention, or to scheduled for those that should be automatically sent with the new RapidPro account.
SMS Settings: Instructions and schema for defining SMS settings
Trigger calls and SMS from within the form, or send an SMS once submitted
Overview of the possible states of SMS messages
How to avoid messaging loops
Using unique short codes to identify places and people via messaging